
Aug . 13, 2024 16:06 Back to list
Exploring HPMC and SDS Interactions in Pharmaceutical Formulations for Enhanced Drug Delivery Systems
Understanding HPMC and Its Role in SDS A Comprehensive Overview
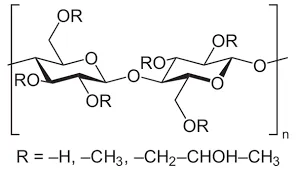
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC), a versatile cellulose derivative, has gained significant attention in various sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. One of its critical applications lies in the formulation of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) products, a widely used anionic surfactant. This article explores the characteristics of HPMC, its interaction with SDS, and the implications of this combination in different industrial applications.
HPMC is a non-ionic, water-soluble polymer derived from cellulose. Its unique properties, including thermal gelation, film-forming ability, and rheological behavior, make it an essential ingredient in many formulations. Due to its high viscosity and adhesive qualities, HPMC is commonly used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in various applications.
.
When combined, HPMC and SDS exhibit an intriguing synergy that enhances their individual characteristics. The interaction between HPMC and SDS can lead to improved viscosity and stability in formulations. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the combination of HPMC and SDS is often used to formulate drug delivery systems. The viscosity-enhancing properties of HPMC can help control the release rate of active pharmaceutical ingredients, while SDS aids in drug solubility, ensuring better bioavailability.
hpmc sds
In the cosmetics industry, the HPMC-SDS combination is pivotal in the formulation of skin and hair care products. HPMC acts as a film-former, creating a protective layer on the skin or hair, while SDS contributes to cleansing and foam formation. Together, they allow for the creation of products that not only cleanse but also condition, providing enhanced performance compared to formulations using either ingredient alone.
Moreover, HPMC can improve the sensory properties of products containing SDS. Many consumers prefer products that feel smooth and have a pleasing texture. HPMC’s thickening and stabilizing effects can help achieve desirable viscosities and textures, enhancing the overall user experience. This interplay between HPMC and SDS is crucial in formulating products that meet consumer expectations for both functionality and aesthetics.
In the food industry, HPMC is used as a food additive, providing texture and acting as a stabilizer in emulsions. When combined with SDS, it can help improve the stability of emulsified products, allowing for more extended shelf life and better quality. This is particularly significant in products like sauces, dressings, and beverages, where maintaining uniformity and preventing separation are essential.
In conclusion, the interplay between Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) showcases the potential of utilizing advanced materials to enhance product formulation across various industries. Whether in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, or food, the combination of HPMC and SDS offers improved stability, texture, and performance. As research into these materials continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications that leverage their unique properties, ultimately benefiting both manufacturers and consumers alike. The future promises exciting developments in product formulation, driven by a deeper understanding of chemical interactions and material science.
-
Versatile Hpmc Uses in Different Industries
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Redispersible Powder's Role in Enhancing Durability of Construction Products
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Applications Driving Green Industrial Processes
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Exploring Different Redispersible Polymer Powder
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Choosing the Right Mortar Bonding Agent
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Applications and Significance of China Hpmc in Modern Industries
NewsJun.19,2025







