
Sep . 28, 2024 11:27 Back to list
Exploring the Role of Cellulose and HPMC in Modern Applications and Innovations
Understanding the Role of Cellulose and HPMC in Modern Applications
Cellulose is one of the most abundant organic polymers found in nature, primarily derived from plant cell walls. It plays a critical role in various industries due to its unique structural properties and benefits. The emergence of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) as a derivative of cellulose has further expanded its applications, particularly in pharmaceuticals, construction, and food industries.
Cellulose Nature's Versatile Polymer
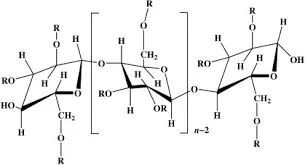
Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of linear chains of glucose units linked by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds. This structure allows cellulose to form strong fibers, providing mechanical strength and rigidity to plants. The renewable nature of cellulose makes it an environmentally friendly resource, and its biodegradability addresses many sustainability concerns prevalent in the modern world.
In various applications, cellulose is modified to enhance its functionality. Its derivatives, like carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and HPMC, serve specific roles. HPMC, in particular, is created by the hydroxyl and methoxy substitution of cellulose, altering its properties and expanding its usability.
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC)
HPMC is a non-ionic, water-soluble polymer that offers a unique set of properties beneficial for a wide range of industries. It is odorless, tasteless, and non-toxic, making it suitable for numerous applications, particularly in areas that demand high purity and safety standards.
One of the standout features of HPMC is its viscosity-imparting ability. When dissolved in water, it forms a viscous gel that can control the flow properties of solutions, making it an ideal candidate for use as a thickener and stabilizer in many formulations. Its ability to form films also makes it useful as a coating agent in pharmaceuticals and food industries.
Applications of HPMC in Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical sector, HPMC is extensively used as an excipient in drug formulations. Its properties enhance the solubility and bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). HPMC is particularly valuable in the development of controlled-release formulations, where the release rate of the drug can be modulated by adjusting the HPMC concentration. This capability ensures that patients receive a consistent and effective dosage over an extended period.
celulosa hpmc
Moreover, HPMC is utilized in the manufacturing of various dosage forms, including tablets, capsules, and hydrophilic gels. Its role as a binder enhances the mechanical strength of tablets, while its film-forming properties aid in the protection and stability of sensitive APIs.
HPMC in Construction and Building Materials
The construction industry has also embraced HPMC due to its versatile properties. It acts as a vital additive in cement-based mortars, providing improved workability, water retention, and adhesion. The presence of HPMC in these mixtures ensures that the materials remain workable for longer periods, allowing for easier application and finish of construction projects.
Furthermore, HPMC contributes to the durability of construction materials, enhancing their resistance to cracking and environmental factors. As urbanization continues to rise, the demand for resilient and sustainable building materials only increases, making HPMC a critical ingredient in modern construction practices.
Food Industry Applications
In the food sector, HPMC is used as a food additive, where it serves various purposes such as thickening, emulsifying, and stabilizing. It is often found in low-fat and reduced-calorie products, where it mimics the mouthfeel of fat without the added calories. HPMC's ability to form gels also aids in developing texture and viscosity in sauces, dressings, and desserts.
Additionally, HPMC is recognized for its use in vegetarian and vegan products as a binder and filler. Its non-ionic nature ensures it is safe for consumption, making it a popular choice among manufacturers catering to health-conscious consumers.
Conclusion
In summary, cellulose and its derivative, HPMC, demonstrate remarkable versatility and functionality across various industries. With the increasing emphasis on sustainable practices and the demand for innovative materials, the applications of cellulose and HPMC are likely to expand further. Their unique properties not only enhance product performance but also offer eco-friendly solutions, positioning them as vital components in the future landscape of numerous sectors. As industries continue to innovate, the role of cellulose and HPMC will undoubtedly remain significant in driving advancements in materials science and technology.
-
Versatile Hpmc Uses in Different Industries
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Redispersible Powder's Role in Enhancing Durability of Construction Products
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Applications Driving Green Industrial Processes
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Exploring Different Redispersible Polymer Powder
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Choosing the Right Mortar Bonding Agent
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Applications and Significance of China Hpmc in Modern Industries
NewsJun.19,2025







