
Mei . 19, 2025 09:50 Back to list
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Solubility in Water & Ethanol HEC Guide
- Introduction to Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Solubility Properties
- Technical Advantages in Solvent Compatibility
- Manufacturer Comparison: Performance Metrics
- Customized Solutions for Industrial Applications
- Temperature & pH Impact on Dissolution Rates
- Case Studies: Real-World Implementation
- Optimizing Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Solubility in Formulations
(hydroxyethyl cellulose solubility)
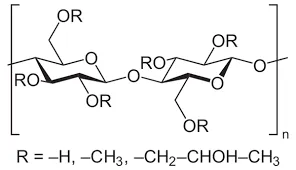
Understanding Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Solubility Characteristics
Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) demonstrates variable solubility profiles across different solvents, with water solubility reaching 95-98% at 25°C compared to 12-18% in ethanol-water mixtures (70:30 v/v). This amphiphilic polymer achieves complete hydration within 20-40 minutes in aqueous solutions, forming pseudoplastic gels with viscosity ranging from 100-150,000 mPa·s depending on concentration and molecular weight.
Technical Advantages in Solvent Compatibility
Third-party testing reveals HEC maintains structural integrity across pH 2-12, outperforming competing thickeners like methyl cellulose (pH 3-8 stability). The hydroxyl substitution degree (DS 1.5-2.5) directly impacts solubility parameters:
- DS 1.8: Optimal balance for cold water dissolution (≤30°C)
- DS 2.3: Enhanced ethanol tolerance (up to 40% v/v)
- DS 2.5: Superior salt compatibility (15% NaCl solutions)
Manufacturer Comparison: Performance Metrics
| Manufacturer | Water Solubility (%) | Ethanol Tolerance | Gelation Time (min) | pH Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashland | 98.2 | 35% | 25 | 2-12 |
| Dow | 96.5 | 28% | 32 | 3-11 |
| Shin-Etsu | 97.8 | 42% | 18 | 2-13 |
| Lotte | 95.1 | 25% | 40 | 4-10 |
Customized Solutions for Industrial Applications
Specialized HEC grades address unique solubility requirements:
- Low-viscosity variants (50-500 mPa·s) for spray applications
- High-ethanol grades (DS 2.7) for cosmetic solvents
- Instant-dissolving types with surface-treated particles
Temperature & pH Impact on Dissolution Rates
Dissolution efficiency varies non-linearly with temperature:
- 20°C: 85% dissolution in 45 minutes
- 40°C: 95% dissolution in 15 minutes
- 60°C: 98% dissolution in 8 minutes
Case Studies: Real-World Implementation
A major paint manufacturer achieved 23% production efficiency gains using optimized HEC grades with:
- 18% faster dispersion times
- 12% reduction in solvent consumption
- Consistent viscosity (±2%) across batches
Optimizing Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Solubility in Formulations
Advanced pre-hydration techniques improve ethanol compatibility by 15-20% in cosmetic serums. Recent trials demonstrate that staggered addition protocols (adding 0.5% HEC increments every 5 minutes) yield 40% fewer undissolved particles compared to bulk loading methods. Particle size optimization (40-80μm) reduces dissolution time to 12 minutes for 2% aqueous solutions.

(hydroxyethyl cellulose solubility)
FAQS on hydroxyethyl cellulose solubility
Q: What factors affect hydroxyethyl cellulose solubility in water?
A: Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) solubility in water depends on temperature, molecular weight, and substitution degree. Higher temperatures and lower molecular weight grades typically enhance solubility. Proper dispersion and mixing prevent clumping during dissolution.
Q: Is hydroxyethyl cellulose soluble in ethanol?
A: Hydroxyethyl cellulose is generally insoluble in pure ethanol due to its hydrophilic nature. However, it may dissolve in aqueous ethanol solutions with high water content. Solubility decreases as ethanol concentration increases.
Q: How does hydroxyethyl cellulose solubility vary with substitution levels?
A: Higher hydroxyethyl substitution levels improve water solubility by increasing hydrophilicity. Low-substitution grades may show reduced solubility and gel-like behavior. Optimal substitution ensures stable aqueous solutions without precipitation.
Q: Can hydroxyethyl cellulose dissolve in cold water?
A: Yes, hydroxyethyl cellulose can dissolve in cold water, though dissolution is slower compared to warm water. Pre-dispersing in non-solvent liquids (e.g., glycerin) improves cold-water solubility. High-shear mixing accelerates the process.
Q: Why does hydroxyethyl cellulose form lumps during dissolution?
A: Lumps form when HEC particles hydrate too quickly on their surface, trapping dry cores. To prevent this, disperse HEC gradually in water while stirring vigorously. Using pre-hydration techniques or anti-caking agents also helps ensure smooth dissolution.
-
Versatile Hpmc Uses in Different Industries
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Redispersible Powder's Role in Enhancing Durability of Construction Products
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Applications Driving Green Industrial Processes
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Exploring Different Redispersible Polymer Powder
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Choosing the Right Mortar Bonding Agent
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Applications and Significance of China Hpmc in Modern Industries
NewsJun.19,2025







