
Дек . 04, 2024 09:16 Back to list
hydroxypropyl methylcellulose uses in tablets
The Role of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose in Tablet Formulations
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a versatile polymer extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in tablet formulations. As a semi-synthetic derivative of cellulose, HPMC is favored for its unique properties, including its ability to serve as a binding agent, film coating, and controlled-release excipient. This article delves into the various uses and benefits of HPMC in tablet formulations, examining its critical role in enhancing the performance and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Binding Agent
One of the primary functions of HPMC in tablet formulations is its role as a binding agent. In the direct compression method of tablet manufacturing, HPMC helps to ensure that the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients adhere together, forming a solid tablet. This is particularly important because the cohesion of powder blends directly affects tablet hardness and disintegration time. The perfect balance of hardness ensures that the tablets do not crumble during handling and can withstand the pressures of packaging and transportation.
HPMC's binding ability is attributed to its high water retention capacity, which promotes adhesion between particles in the formulation. When mixed with water or other solvents, HPMC forms a gel-like consistency that enhances the flow properties during the compression process. This feature significantly aids in producing tablets with consistent weight and size, minimizing variability among batches.
Film Coating Agent
Another significant application of HPMC is in film coating systems. Film coatings serve to improve the aesthetic appeal of tablets while providing protection against environmental factors like moisture and light. HPMC is often utilized in aqueous film coating formulations due to its ability to form transparent and smooth coatings that are free from cracks and imperfections.
Moreover, HPMC film coatings can modify the release profile of the APIs. By adjusting the thickness and composition of the coating, manufacturers can control the rate at which the drug is released in the gastrointestinal tract. This controlled-release property is particularly valuable in ensuring that the medication remains effective over an extended period, minimizing the frequency of dosing and improving patient compliance.
hydroxypropyl methylcellulose uses in tablets
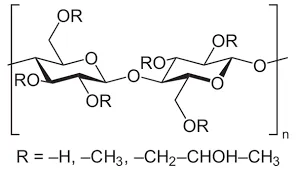
Controlled Release and Sustain Release Applications
HPMC is widely recognized for its use in controlled and sustained-release formulations. When incorporated into matrix tablets, HPMC helps create a matrix system that regulates the release of the active ingredients over time. The polymer swells upon contact with gastrointestinal fluids, forming a gel layer that modulates the diffusion of the drug from the matrix into the surrounding environment.
This controlled release mechanism not only enhances the bioavailability of APIs but also helps maintain therapeutic drug levels in the bloodstream, reducing the peaks and troughs associated with immediate-release formulations. Consequently, patients benefit from more stable and prolonged therapeutic effects while minimizing the side effects associated with fluctuating drug levels.
Compatibility and Stability
One of the significant advantages of using HPMC in tablet formulations is its compatibility with a wide range of APIs and excipients. HPMC is chemically stable and exhibits low toxicity, making it suitable for various pharmaceutical applications. Its non-ionic nature reduces the potential for interactions with other formulation components, ensuring that the stability and efficacy of the final product are maintained.
Additionally, HPMC does not undergo significant thermal degradation during the tablet manufacturing process, which is crucial for preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive APIs. This characteristic is vital for formulating tablets that retain their potency and effectiveness throughout their shelf-life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is an invaluable ingredient in the formulation of tablets. Its multifunctional role as a binding agent, film coating material, and sustained-release excipient significantly enhances the performance and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the demand for excipients that improve drug delivery systems will persist, positioning HPMC as a critical component in innovative tablet formulations. By leveraging the unique properties of HPMC, manufacturers can create effective, reliable, and patient-friendly therapeutic options that meet the needs of modern healthcare.
-
Versatile Hpmc Uses in Different Industries
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Redispersible Powder's Role in Enhancing Durability of Construction Products
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Applications Driving Green Industrial Processes
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Exploring Different Redispersible Polymer Powder
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Choosing the Right Mortar Bonding Agent
NewsJun.19,2025
-
Applications and Significance of China Hpmc in Modern Industries
NewsJun.19,2025







